When creating a budget, individuals should prioritize essential expenses first, including housing, utilities, food, and healthcare costs. Next comes establishing an emergency fund covering at least three months of expenses, followed by high-interest debt repayment. After securing these financial foundations, people can allocate funds toward long-term savings goals and discretionary spending. Using the 50/30/20 rule provides structure, dedicating fifty percent to needs, thirty percent to wants, and twenty percent to savings. Understanding these priorities creates sustainable financial success.

How does one transform the overwhelming task of managing money into a clear, actionable plan that aligns with personal priorities and financial aspirations? The answer lies in understanding what to prioritize when creating a budget, starting with a thorough assessment of income and expenses.
The foundation of effective budgeting begins with calculating accurate net income and meticulously tracking all spending. Individuals should categorize expenses into fixed costs like rent and utilities, and variable expenses such as entertainment and dining. Using apps, spreadsheets, or manual recording methods helps gather detailed spending data over several weeks, while reviewing bank and credit card statements ensures precise categorization. Leveraging document management systems can streamline the organization and retrieval of financial records, enhancing budgeting accuracy.
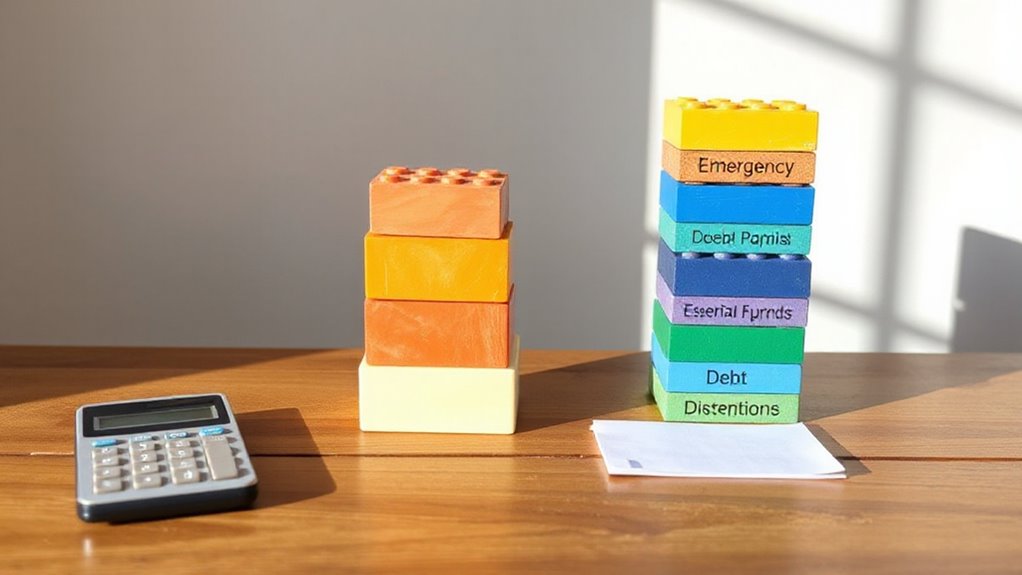
Once spending patterns are clear, setting and prioritizing financial goals becomes essential. Successful budgeters define realistic short-term and long-term objectives, quantifying each goal by specifying the total amount needed, target date, and required monthly savings. Emergency funds should take precedence, covering at least three months of essential expenses before pursuing other goals. High-interest debt repayment ranks as another critical priority, particularly for unsecured debts that compound quickly.
Emergency funds covering three months of expenses must take precedence before pursuing any other financial goals or debt repayment strategies.
Budget allocation requires distinguishing between needs and wants. Essential expenses like housing, food, healthcare, and utilities must be covered before discretionary spending. This differentiation helps identify areas for potential savings without compromising necessities. Setting realistic spending limits for each category maintains control over variable expenses while ensuring sustainability. The 50/30/20 rule provides a structured framework that allocates fifty percent for needs, thirty percent for wants, and twenty percent for savings and debt repayment.
Data-driven approaches enhance budget effectiveness through scoring systems that evaluate cost efficiency and performance potential. Specific, measurable, time-bound goals aligned with overall financial objectives provide clear direction. Regular monitoring through tracking systems allows for prompt adjustments when circumstances change. Implementing a 24-hour cooling-off period before major purchases helps reduce impulse spending and maintains budget discipline.
Managing limited resources demands strategic flexibility. Breaking down large expenses into smaller, manageable portions improves tracking accuracy and identifies cost-saving opportunities. Conducting cash flow analysis for long-term commitments ensures annual funds align with strategic plans.
Successful budgeting ultimately requires treating savings goals as essential line items rather than afterthoughts. By prioritizing emergency funds, debt repayment, and basic needs while maintaining flexibility for unexpected changes, individuals create sustainable financial plans that support their long-term prosperity and peace of mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should I Review and Update My Budget Priorities?
Individuals should review budget priorities monthly for ideal financial management, with weekly check-ins during periods of income fluctuation or financial instability.
Major life events like job changes, marriage, or unexpected expenses trigger immediate budget updates.
Annual thorough reviews help assess long-term progress toward financial goals.
Regular monitoring strengthens spending discipline and financial confidence, while budgeting apps can facilitate consistent tracking and engagement with personal finances.
What Percentage of Income Should Go Toward Emergency Funds Versus Debt Repayment?
The ideal allocation between emergency funds and debt repayment depends on individual circumstances and debt interest rates.
Financial experts typically recommend following the 50/30/20 rule, allocating 20% of income toward savings and debt repayment combined.
However, high-interest debt above 7-10% should generally take priority over building large emergency funds, while those with unstable income may need to emphasize emergency savings first.
Should I Prioritize Paying off Low-Interest Debt or Investing for Retirement First?
One should prioritize securing any available employer 401(k) match first, as this represents guaranteed returns that exceed most low-interest debt costs.
After capturing the full match, individuals can focus on paying off debt below 6% interest rates more gradually while continuing retirement contributions.
This balanced approach maximizes the employer’s free money while building long-term wealth through compound growth, making both goals achievable simultaneously.
How Do I Budget for Irregular Expenses Like Car Repairs or Medical Bills?
Budgeting for irregular expenses requires systematic planning and dedicated preparation. One should review past bank statements to identify patterns.
Then calculate average monthly costs by dividing annual totals by twelve. Establishing separate savings accounts for categories like automotive, medical, and home maintenance helps organize funds effectively.
Automating monthly transfers ensures consistent funding, while treating these amounts as fixed budget line items prevents financial surprises.
What Budgeting Apps or Tools Are Best for Tracking Spending Priorities?
For tracking spending priorities effectively, You Need a Budget (YNAB) excels with zero-based budgeting that assigns every dollar a purpose.
While Goodbudget’s envelope method helps maintain category discipline.
Monarch offers extensive goal tracking with customizable dashboards.
And PocketGuard provides real-time spending alerts.
Users should prioritize apps with strong categorization features, spending insights, and goal-setting capabilities that align with their financial priorities and budgeting style.